Good heating in both a private house and an apartment is characterized by several signs. Firstly, all rooms should be warmed up to a comfortable temperature and the latter should not fluctuate depending on the time of day. Secondly, fuel consumption should be kept to a minimum. Thirdly, it is desirable to be able to adjust the intensity of heating the batteries in each room. Fourth, repairs, if required, should be simple, easy and carried out without turning off the heating of the entire house.
Types of heating
The principle of operation of any heating system is that the coolant, water or antifreeze, is heated in the boiler, moves through pipes from one heating device to another, gradually transferring heat, and returns to the boiler for re-heating and use. However, there are several ways to implement this concept. The choice of option that is optimal for a private home depends on a number of factors.
Essential for the classification is the device of the expansion tank. Water, like any other liquid, expands when heated and, accordingly, its density decreases. An expansion tank is installed to compensate for the effect.

Depending on the design of the tank, the systems are divided into two large groups.

Natural circulation
Any heating scheme, first of all, must ensure the supply of heated coolant to batteries or radiators. There are two methods to implement movement.
Natural circulation is an economically advantageous option, as it will require a minimum of equipment. In this case, the circulation of water is ensured by the property of expansion of water or other liquid after heating. A heat carrier with a high temperature has a lower weight and moves along the upper pipe to the radiators, where it is gradually cooled. Cooled, it goes down and returns to the boiler along the return pipe, simultaneously displacing the heated, lighter heat carrier. The magnitude of the natural circulation will depend on the temperature difference (usually 10 degrees), and on the resistance to movement of the coolant. The last problem is solved by increasing the diameter of the pipe.

Also, the heating efficiency is ensured by the level of the arrangement of elements: the boiler must be lower than the level of radiators by at least 3 m.
Benefits
- Profitability - minimum equipment required.
- A fairly simple DIY installation.
- If necessary, in order to switch to forced circulation, it is enough to put the pump into processing.
disadvantages
- Such heating has significant inertia and is practically unregulated.
- For the implementation of the project, certain conditions must be met: the area of \u200b\u200ba private house should not be more than 3,500–3,600 square meters. m. The boiler must be located significantly below the radiators.
Despite the above disadvantages, heating by type of natural circulation is the best option for a one- or two-story house. The photo shows a diagram for a two-story building.

Forced circulation
The difference of this system is that the intensity of movement of the coolant is ensured by the operation of the pump, which in turn entails both advantages and disadvantages. But thanks to the use of the pump, this principle is often implemented for a closed circuit.
- The installation is still simple enough to be done by yourself. The only difference is the insert of the pump. The device is connected last and certainly in the return pipe, as it is designed for a liquid temperature of not more than +60 degrees.
- There is no need to observe the difference in the location of the radiators and the boiler.
- Installation is possible in a private house of any size.
- It is possible to adjust the temperature.
Organization of heating by the principle of forced circulation has its own drawbacks.
- Higher heating costs.
- Dependence on the current supply - the pump is connected to the mains, and in the absence of current the house will not be heated. The video shows the installation process of the pump.

Installation of a closed heating system
Before proceeding with the installation, preliminary calculations should be made. They can be done by hand and include a number of parameters.
- Calculation of power, based on an approximate ratio: 1 sq m area - 1 kW.
- Calculation of the power of radiators - for this you need to use the passport of the device.
- The choice of pipes, and the assessment of resistance by the size of the pipe section.
- Choosing a boiler of the appropriate capacity and expansion membrane tank.
When installing heating in a closed circuit, carefully follow the recommendations. The video demonstrates the installation of a variant with one pipe and a circulation pump.
Everyone knows that heat needs to be saved and it is beneficial. But few people understand how to do this in practice, in a real residential building. However, sooner or later, such knowledge will be useful to all owners, since it is for them to decide on the composition of the overhaul.
1. Everyone needs different heat requirements: someone feels comfortable at + 21 ° C, while someone needs + 26 ° C. However, residents cannot regulate heat consumption in accordance with their preferences.
2, Useful, for which the owners really have to pay, is only part of the thermal energy they receive. The system works in such a way as to exclude complaints of underheating, while the rest are saved from overflows by opening the windows. Those surpluses of heat that are thus dissipated into the atmosphere, as well as heat loss through walls, foundations and roofs, are money thrown away.
3. The amount of heat supplied to the house is regulated by outdated standards that do not take into account the real condition of buildings and heating networks, their wear.
4. In many cases, especially if the house is old, there is a real problem of heat loss: through cold walls, poorly insulated cellars and roofs, old wooden windows. Of course, heat losses through building envelopes are not directly related to the problems associated with heat supply; in the end, they affect the efficiency of heat use as critically as other factors.
5. There is another problem, which is not so obvious in a superficial study of the issue, but, nevertheless, is very significant: this is an uneven distribution of heat throughout the house. This is explained by the fact that the hydraulic resistance of the heating system increases with distance from the heat input, so the risers distant from it warm up worse, and the closest ones excessively. If the system’s work is adjusted according to the average parameters for the house, it turns out that someone wastes heat, scattering it through the windows, and someone freezes at the same time.
6. For all these problems, owners pay for heat, based only on the area of \u200b\u200btheir apartments, regardless of how much real heat they need and how much they consume it.
In order to limit the heat consumption to the amount really necessary for the residents of the house, and to give each owner the opportunity to regulate this amount at the level of his apartment, special technical solutions are needed that are implemented either during the construction of the house or in the process of major repairs:
1. First of all, this is home regulation in general, for example, depending on changes in weather conditions or the time of day. Such regulation is carried out by the automation of an individual heat point based on changes in the air temperature in the street.
2. In order to solve the problem of uneven supply of coolant to risers different from the heat input, special devices are used - automatic balancing valves. They are installed on each riser after the installation of a heat point and equalize the amount of hot water, and hence the heat entering these risers. Thus, everyone receives the same heating service and there is no cost overrun.
3. Finally, everyone can set a comfortable air temperature in the rooms using automatic radiator thermostats, because everyone has different preferences. And if at the same time also switch to the apartment metering of heat, then at the end of the month, residents who consume different amounts of heat will pay differently. This is not only fair, but also encourages even greater savings. For example, leaving for the country, you can limit the air temperature in the apartment to 14 ° C.
The only problem remains the organization of a truly fair apartment-by-house heat metering, when everyone pays only for what he has consumed. The fact is that you can install individual heat meters in apartments only if each of them has a single heat input from a common riser, usually located in a common hall, and all heating devices in the apartment are connected to this input. It is at the input that a heat meter is installed. This is called the horizontal floor wiring of the heating system. Unfortunately, in Russia, houses with such wiring were not built practically at all before, but now there are very few, with a strength of 20%, and basically this is the so-called "elite" housing.
In most of the domestic standard panel high-rise buildings implemented vertical riser wiring of the heating system. How it works, everyone knows well: risers penetrate the house directly through the rooms, and a heating device is connected to each. For such a scheme, a fundamentally different solution is needed, and it exists.
A radiator distributor is mounted on each radiator, which measures the heat transfer of the heater. Knowing the power of each of them (it is determined by the design of the house) and the total consumption for the month, it is possible to calculate the share of each radiator in the common house consumption from the data received from the distributors. Summing up apartment by apartment, we get the individual consumption of each owner per month.
The equipment can work automatically. For example, the Danfoss INDIV AMR apartment-by-house heat metering system collects readings from distributors over the air to floor and access concentrators, and then transmits them via the Internet to a billing center where heat bills are automatically generated.
It is impossible to switch to this form of accounting individually, since at least half of the residents must install radiator valves. Such decisions require discussion at the general meeting and can be implemented just during the overhaul, along with the modernization of the heating system.
Having the necessary knowledge, the owners can make the right decision on the composition of the overhaul and get real savings in heat and money. In addition, each of them, thanks to the automation installed in the house, radiator thermostats and distributors, will be able to pay only for their personal consumption and save even more.
In a private house, you can use various types of heating, it will depend on their choice heating system operation.
The principle of the heating system
The principle of operation of an open-type water heating system (Fig. 1). The water heated in the boiler moves to the heating devices and back under the influence of hydrostatic pressure. It occurs due to the density difference between the heated and cooled liquid. Hot water from the boiler, as lighter, rises up the main supply riser. From it, it enters the distributing pipelines and through the supply risers to the heating devices. Where the water cools down, as a result of which it becomes heavier and with its weight displaces hot water through the return line from the heating boiler to the main riser. therefore heating system operation with natural circulation occurs only due to the constant heating of water in the boiler. Such a system cannot be used in buildings with a large length and pipes of significant diameters are needed for its manufacture.
The principle of operation of the water heating system closed type (Figure 2) is devoid of the above disadvantages. In it, water circulation occurs due to the operation of a centrifugal pump in a closed heating system. In this case, the pump can either be located in the boiler body, or it can be installed in the return heating line, often in front of the boiler. In such a system, the heated water from the boiler moves through the pipes to the heating devices and is returned using a centrifugal pump. Watch the video.
One of the modern types of heating is the "warm floor" system. System operation heating It is based either on heating an electric cable or a pipe included in a water heating system and laid in a screed. In the off-season, when it is not rational to use heating, or in its absence, electric heaters (convectors) help out (Photo 1). One of the positive qualities of which is that convectors do not burn oxygen and can be used as the main source of heating. Like electric heaters (convectors), fan heaters are used (Photo2). They quickly and directionally move heated air around the room.
The operation of the heating system directly depends on the correct and effective selected type of heating at home.
Today, more and more people are moving from city apartments to suburban areas. This is largely due to the fact that the welfare of the inhabitants is growing, opening up new, previously inaccessible opportunities. And the cost of suburban real estate was equal, and sometimes it became lower than the cost of a good apartment in the city center. This and much more, as well as the availability of own vehicles, played a decisive role in the fact that people began to choose peace and solitude, voluntarily abandoning such "charms" of city life as drinking neighbors, parking wars, strange people under the windows, and like.
The heating system without a circulation pump works by itself, regardless of the availability of electricity in the house.
However moving to a private house, together with the joy of owning property and fresh air, gives its owner a whole range of tasks to which he had absolutely nothing to do before, entrusting them to the hands of special communal services: cleaning the local area, garbage removal and heating.
Let's talk about what a closed heating system is, what it consists of and how it works, so that at least one question in the head of a happy landowner becomes smaller.
Basic operating principle
First of all, you need to understand what kind of option is being discussed: the heating system without a circulation pump works itself, regardless of the availability of electricity in the house, this is good, but there is a drawback - the need to pull twice as many pipes and their weak and slow heating. Another thing is a closed-type heating circuit with a circulation pump, which has a huge handicap - heating takes place much faster, there are more laying possibilities, in a word, some pluses. But first things first.
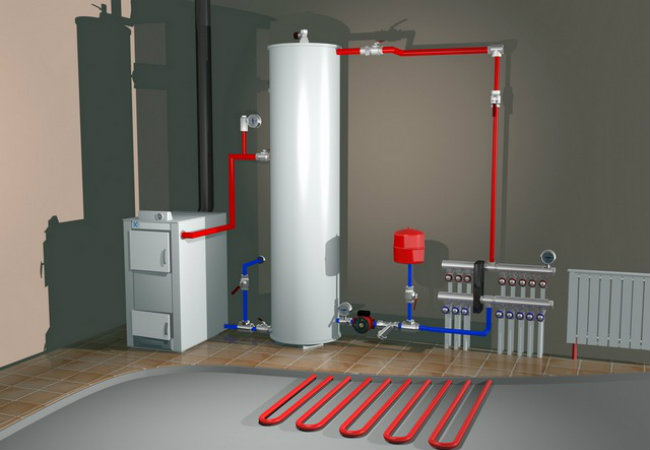

The closed-type heating system with a pump compares favorably with the gravity-flowing version in that the movement of the heat carrier along it is controlled and controlled by a pump.
Without pump
This option is perfect for single-story buildings of a small area. The main advantage of the system is its autonomy. Water, heating in the boiler, rises through the pipes. Then it passes the path along the horizontal riser supplying the coolant to the radiators. From the radiators, the cooled water goes down to the lower line leading back to the boiler, and the cycle repeats again.
Pipes are placed at a slight slope, from top to top, from left to right, and from bottom to left, the bottom pipe, along which the cooled coolant is discharged. Expansion tank in this case, it is installed at the lowest point of the system; its main purpose is to prevent pressure surges and compensate for them. The pressure inside the network is constantly changing dynamically, this is due to the fact that the water expands when heated, and decreases when it cools.
A pump will still be needed at the stage of filling the system with water. Pipes are filled until the working pressure is reached, which, as a rule, is one and a half atmospheres.
With pump
The closed-type heating system with a pump compares favorably with the gravity-flowing version in that the movement of the coolant through it is controlled and controlled by means of a pump, which, in turn, allows:
- Choose the pipe layout option that is most suitable for your case;
- Carry out several heating circuits, for example, on the first and second floors separately;
- To regulate the temperature in all rooms, without affecting the movement of the coolant and without reducing the performance of the entire system.
Closed heating is best done with a pump. In rare cases, installation closed heating without a pump, they perform in a hybrid way. The pump is present in such cases, but it is cut in such a way that in the event of a power outage, the system can switch to autonomous operation. Nevertheless, all the disadvantages of a gravity-fed circuit will invariably accompany such a connection.
Pipe Layout Options
Scheme closed system heating with a pump gives you several possible options for connecting heating.
Single tube
This method can be performed in different ways. Here are the basic ways to connect a one-pipe circuit:
- Sequential circuit. In this case, the coolant moves through the network from the radiator to the radiator, gradually cooling, and on the last heating element it almost ceases to do its job;
- Leningradka. Named so because it was first developed and implemented in Leningrad. It consists in the fact that radiators are connected from the bottom to a riser that runs horizontally, along the floor or under it. Installing needle valves at the inlet and outlet of the radiator will allow it to be disconnected from the network for repair work, without disturbing the general circulation, and installing an additional valve on the jumper under it will allow you to adjust the pressure and velocity of the coolant through the network, achieving the required temperature.
In addition, there is also a scheme mentioned at the beginning of the article in which hot water is supplied from above the riser horizontally located below the ceiling or behind it and, passing through radiators, goes back to the pump.
Double pipe
This connection allows you to achieve the supply of coolant to each heating element separately, without loss of pressure, speed and temperature, the removal is also performed separately for each radiator. This allows you to install special rheostats on each device, adjusting the temperature individually for each radiator.
This option is more preferable, since it allows you to configure the thermoregulation in the building, taking into account the individual needs of each consumer, which gives significant savings in money and resources.
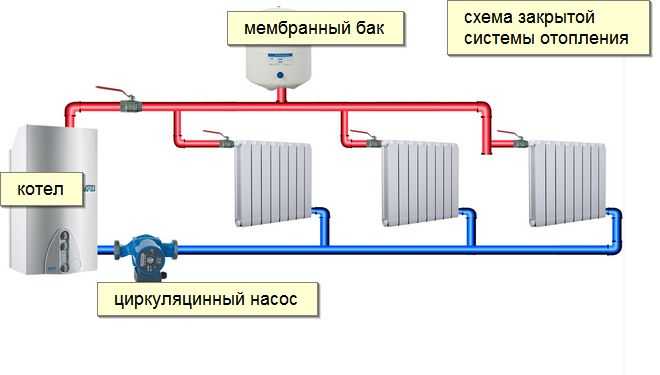
This connection allows you to achieve the supply of coolant to each heating element separately, without loss of pressure, speed and temperature.
Important details
Independent of how the connection will be made: with or without a pump, a single-pipe circuit or a two-pipe system - there are several units, the presence of which is mandatory for a closed heating system:
- Boiler. It must be selected for the operating parameters of the system. Be sure to check the operating pressure range in the boiler - it must meet your requirements;
- Expansion tank closed. It should be equal in volume to one tenth of the capacity of the pipe network. It is installed at the bottom of the system, in front of the pump, if any. The tank compensates for the pressure inside the network and is one of its most important elements. Indeed, when heated, the water expands, while cooling, it shrinks - all this causes constant pressure drops inside the pipes. It is the tank that compensates for these differences, take your choice very carefully. Do not confuse - for heating networks, the tank should be red;
- Mayevsky cranes on radiators and an automatic bleed air valve mounted on a vertical outlet, after the tank, in front of the pipe network. A mandatory element that allows you to remove excess air, which will necessarily appear during the operation of the system. Mayevsky cranes allow to withdraw air jams from radiators;
- Pressure gauge and emergency coolant relief valve. They are placed on a vertical outlet, after the boiler, in front of the main heating network. A pressure gauge allows you to control the pressure inside the pipes, and the valve will come to the rescue if this value exceeds the permissible limits.
The listed items must be of the highest quality, purchased from authorized representatives of well-known brands and have warranty service. The performance of the entire system depends on them. Do not save on “trifles” and your heating will last you for many years!







The best material for car trim
Principles of hardening the body
Do-it-yourself compressor - with minimal scrap costs
Which is better: do-it-yourself or factory-made compressor for painting a car
Causes of fuel pump malfunctions