If it is necessary to lay pipes outside buildings, it is most reasonable to place them in the ground. However, this option requires additional protection of the pipeline - from cold and moisture.
This is done to extend its service life, as well as to prevent freezing of the fluid flowing inside.
Article Content
Why isolate?
When laying a pipe outside the building, moisture and low temperatures can adversely affect it (and the medium flowing inside). In addition, some materials (polymer) quickly become unusable and lose their quality when exposed to direct sunlight.
Also, the pipeline may be damaged by actions (intentional or unintentional person).
Pipes are preferably laid in the ground for the following reasons:
- To prevent the negative factors mentioned above.
- In order not to create a communications network (which will take up space, interfere with the passage / passage) on the surface.
When laying a line underground, the following dangerous factors remain relevant:
- Possibility of freezing the fluid flowing inside.
- The possibility of corrosion of the pipe itself - from exposure to moisture.
The first factor is relevant in winter: the depth of soil freezing in most Russian regions reaches (and exceeds) 1 meter. That is, so that the flowing medium does not freeze in the cold - pipes should be laid in the ground deeper than this indicator.
This is often inconvenient: further maintenance of the line becomes more complicated (if you need to check or repair, you will have to dig a deep trench), and the cost and time of excavation during installation increases.
The importance of pipeline insulation (video)
About the dangers of lack of isolation
Water and sewage pipes are laid in the ground, both municipal (going from and to apartment buildings), and for private houses and various industrial buildings. It is necessary to use a heater in both cases - since water flows inside these lines.
Often the pipeline is laid, which does not exceed the depth of freezing of the soil. As a result, in severe frost, the liquid in the pipe may freeze, especially if it does not flow continuously and under high pressure.
And it freezes very quickly - in less than an hour, an ice jam forms inside.
Since the pipeline is laid in the ground, to eliminate it, you will have to dig a trench, look for a frozen place and warm it. And all this is in the cold. Moreover, the sewerage or water supply will not work in the house (depending on which line “sits down”).
In addition to the troubles, because the sewerage or water supply system will stop working in the house, when an ice plug occurs, there is also the possibility that the pipe will burst. This happens because when freezing, moisture expands, that is, ice will take up more space than water. As a result, the pipe walls may not withstand.
Eliminating this problem is an even more complicated and less enjoyable task than steaming a frozen area. In winter, in the cold, you’ll have to not only dig a trench (and not a small one, but along the entire line of the pipe to find the damaged part), but also repair the pipe itself. Often this can only be done by completely replacing the cracked segment.
How to isolate?
Laying in the ground, can be performed in several ways:
- The heating electric cable.
- Bulk materials used to dig a trench.
- Heat insulating paint.
Often (but rather vice versa - very often) the methods mentioned above are combined, especially in regions where winters are long and / or very cold.
Electric cable application
Warming with an electric cable is a relatively new option. Compared to the other two - more expensive. Most often, such insulation is used in private residential construction.
The essence of the technology is to use a cable that heats up when current flows through it. It can either be wrapped around a pipe, or placed inside it.

Pipe with foil insulation in the trench
From the positive aspects:
- the ability to control the temperature of the cable, and therefore - the consumption of electricity
- the ability to configure automatic on / off systems depending on temperature;
- simple and quick installation (compared with all other insulation technologies).
Not all systems have the ability to adjust and automatically turn on / off. Such options are more expensive, but as a result they save on electricity: if on the street -5 - it is not necessary to turn on the heating at full capacity.
In terms of installation, such a system is extremely simple: the cable is simply wound around the pipe, after which it is connected to the mains. Moreover, it does not matter whether it is a straight section, a rotary, or a section with a branch.
Among the disadvantages of this solution:
- increase in electricity costs;
- dependence on the stability of the power grid;
Using a cable is not always reasonable in homes with old wiring, or in regions where there is a power outage. The "dead" voltage or lack of electricity will lead to the fact that in severe frost pipes can remain without thermal protection.
As a result, the liquid can freeze quickly. On the other hand, after the restoration of electricity, the ice in the pipe will melt, as the cable heats up again.
Ideally, apply such insulation in combination with any of the other options in case the pipe still freezes. In this case, you don’t have to dig a trench: it will be enough just to turn on the heating, and the ice inside will melt.
Using a cable to heat a pipe (video)
Thermal insulation materials
This option is often used when laying a new line. It can be performed in two ways:
- The shell is a rigid product consisting of two segments that are worn on a pipe section.
- Roll - such material is wrapped around a pipe and fixed on top with a wire.
The insulation can be made of any heat-insulating material:
- Styrofoam.
- EPSP.
- Mineral wool materials.
- Foam rubber.
- The made foam polyethylene.
Often, from above, such a heater is additionally protected by a layer of galvanized steel, a plastic casing, or simply a plastic film. When laying in the ground, this is relevant in order to prevent damage to the heat insulator itself, as well as to protect the material from contact with moisture.

Of the minuses of such insulation is the complexity of processing rotary sections: the shell is intended only for putting on a straight pipe. As an option, such parts of the pipelines (turns, diameter differences, branching, and so on) can be insulated with roll materials.
Bulk materials
The easiest way is to fill the trench in which the pipe lies with materials that leak moisture and cold worse than ordinary earth. It could be:
- Expanded clay.
- Vermiculite.
- Sand (both separately and with sawdust).
- Granular polystyrene foam (foam balls).
- Ecowool.
Such insulation is inexpensive, and is extremely simple. To prevent contact with moisture, before filling it is possible to line the bottom and walls of the trench with a plastic film (especially important if sawdust is used).
Of the minuses, the low efficiency of the small layer can be distinguished: for effective thermal insulation, such a heater should be covered with a thick layer - several tens of centimeters. For this reason, this option almost always acts as an addition to any of the others.
Heat insulating paint
The use of heat-insulating paint is not the most effective option: separately this material is not a serious barrier to cold. However, when laying in the ground, its layer may become additional protection in contact with moisture.

This type of paint can be of the following grades:
- Corundum.
- Astratec.
- Armor.
This material is applied in the same way as regular paint: with a brush on the surface of the pipe, in order to increase efficiency - in several layers. After complete hardening of the coating on top, you can, or any other method of insulation.
PPU spraying
The option is relatively new and expensive, and is mainly suitable for large diameter pipes. The technology consists in spraying liquid polyurethane foam onto a pipeline surface.. Hardening, this material forms a dense crust, which has one of the best indicators of thermal conductivity (0.02-0.03 W / mK).
Frozen PPU is not subject to corrosion, is not afraid of moisture, does not “interest” insects and animals. Among other heat insulators - he is the clear leader.
Among the disadvantages of this technology is the comparative high cost and the ability to be performed only by specialized organizations: equipment for spraying is expensive, and requires knowledge for operation.
Pipelines for heating, water supply and sewage, as a rule, are laid in the ground. The exceptions are communications built in permafrost areas. They are mounted on low or high supports and are carefully insulated.
Is it necessary pipe insulation in the ground? Yes, if it is not possible to lay them below the level of freezing, where a positive temperature is maintained. In Russia, these values \u200b\u200bvary from 0.7 to 2.4 m.
Glass wool, mineral wool slabs, expanded clay are selected as a heater from traditional materials. But they require dry soil or good waterproofing, which leads to an increase in the cost of the process.
Of modern insulation you can offer:
- foam shells
- foamed polyethylene
This insulation for insulation of pipes in the ground is available in the form of half-cylinders, cylinders and tubes, which correspond to the diameter of the pipelines and have different thicknesses of the insulation layer.
Methods of laying pipes in the ground
There are several methods of underground pipe laying:
- A channelless installation in which pipes are buried in a trench in compliance with the necessary rules for excavation and installation. In places difficult to access for technology, the modern trenchless method of deep directional drilling is used.
- In trays, which can be reinforced concrete or, impregnated with an antiseptic, wooden structures placed in a trench.
- In passageways and impassable channels. This method is used by construction and installation organizations when arranging trunk pipelines and is accompanied by concrete work.
How is pipe insulation in the ground
Expanded clay
Despite the large selection of modern heat insulators, public utilities continue to use a backfill made of expanded clay mixed with bitumen. The thickness of the layer of such insulation over the pipes should be 200 mm or more. The convex surface of the backfill is protected by a polymer film, the ends of which on the sides should overlap expanded clay by at least 100 mm.
Glass wool
Rolls of this insulation are wrapped around pipes and fixed with galvanized wire. On top, to protect against moisture, roofing material or fiberglass is fixed in the same way.
Foam shells, polyethylene tubes and basalt wool cylinders
Their installation does not require special skills. Products are put on the pipe and secured with adhesive tape, which is also used for gluing longitudinal seams and joints.
Finally
It should be noted that pipe insulation in the ground should not be limited to a recessed straight line. As practice shows, freezing often occurs at the entrance of the pipeline into the building when it leaves the ground or in an unheated basement. This is a relatively small area, so in the northern regions it makes sense to additionally install a self-regulating heating cable under the insulation, which will save the water supply and sewage in severe frosts.
In each injection of the Russian Federation it is necessary to heat the dwelling in a special period of the year. It is unrealistic to imagine the life of an apartment living in the Russian Federation without a heating complex. Everyone knows that heat sources are constantly increasing in price. Everyone wants to understand: how to modernize the heating complex of the home. On the Internet site there are many different systems for heating the cottage, using completely unique methods of heating production. These heating schemes can be implemented individually or combined.
In the modern world, even the most beautiful and well-designed building will be unusable if all the necessary engineering communications are not laid to it. Heat networks, power supply networks, sewage and water supply networks, gas supply networks - the list of utilities can be continued, and in each case this list can be reduced, or supplemented with new items. But one thing is certain - underground or surface laying of the heating pipeline is necessary for the further operation of the structure, whether it is a production facility, public, administrative, or residential building.
Laying of heating main pipelines
 1. For laying an external sewage, dig a trench. Its depth should allow to lay the pipeline below the level of freezing of the earth, which is present in each climatic zone. For central Russia, it ranges from 1.5 to 1.7 meters.
1. For laying an external sewage, dig a trench. Its depth should allow to lay the pipeline below the level of freezing of the earth, which is present in each climatic zone. For central Russia, it ranges from 1.5 to 1.7 meters.
2. When installing a water supply system, it is possible to dig polypropylene pipes into the ground by 20-30 centimeters. In general, the depth of the trench depends on the climatic conditions in the construction area. For water pipes, the slope is not needed, but for sewer pipes it should be 1 cm of the pipeline in the range from 2 to 2.5 centimeters.
3. When laying in the ground, polypropylene pipes do not require additional insulation. They do not emit harmful substances, are not toxic and will tolerate temperature extremes and chemical effects. Their frost resistance is high and such pipes can tolerate temperatures from 15 to 60 degrees of frost.
4. The space between the walls of the trench and the pipe itself is covered with sand or a mixture of clay and sand. With this mixture, you need to fill the pipe itself and densely tamp its layer so that there is no deformation of the pipeline. After that, you can lay the earth, which was previously excavated from the trench.
5. Mark the location of the pipe in your area. This avoids accidental pipe damage during earthworks.
 1. Polypropylene pipes for heating differ from reinforced standard pipes. They have a layer of aluminum foil transferred to the middle of the polypropylene layer. Therefore, there is no need to clean the aluminum layer. In preparation for welding, the ends of the pipes are simply trimmed, and this ensures a 100% convergence of the ends of the pipe inside the fitting.
1. Polypropylene pipes for heating differ from reinforced standard pipes. They have a layer of aluminum foil transferred to the middle of the polypropylene layer. Therefore, there is no need to clean the aluminum layer. In preparation for welding, the ends of the pipes are simply trimmed, and this ensures a 100% convergence of the ends of the pipe inside the fitting.
2. The heating pipe is also laid below the level of soil freezing.. Outside the city, where gas and electricity supply are unstable, heating systems often freeze. But polypropylene pipes, especially reinforced ones, can withstand this test more easily, because when water freezes in them, they do not crack like iron, but only slightly change in volume, and after thawing they take their original form.
Advantages of polypropylene pipes for external pipelines:
 - resistance to the effects of wastewater with a temperature of up to 95 degrees;
- resistance to the effects of wastewater with a temperature of up to 95 degrees;
Resistance to most aggressive environments that cause corrosion of metal pipes;
- dielectric properties that steel and cast iron do not have;
A small susceptibility to waterjet and this allows the use of polypropylene pipes to drain and transport liquid with solid particles;
A small level of roughness, so polypropylene pipes can be laid with a slight slope and there will be no overgrowing of pipes.
Source: http://truba-info.ru/%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%BA%D0%BB%D0%B0%D0%B4%D0%BA%D0%B0-% D0% BF% D0% BE% D0% BB% D0% B8% D0% BF% D1% 80% D0% BE% D0% BF% D0% B8% D0% BB% D0% B5% D0% BD% D0% BE% D0% B2% D1% 8B% D1% 85-% D1% 82% D1% 80% D1% 83% D0% B1-% D0% B2-% D0% B7% D0% B5 /
 The laying of heating pipes in the ground is often carried out together with pipes of other networks (sewage, drinking water, etc.). When installing the pipeline underground, two methods of laying pipes can be used.
The laying of heating pipes in the ground is often carried out together with pipes of other networks (sewage, drinking water, etc.). When installing the pipeline underground, two methods of laying pipes can be used.
Duct laying
This method of laying a pipeline is used to protect pipes from external influences. When channeling pipes, various types of channels are used:
- Feedthrough channels. They are used in case of simultaneous laying of a large number of pipes. Such a channel allows quick access to pipes for inspection and repair.
- Semi-passage channels. The construction of canals of this type is required if rare access is required to the pipeline.
- Impassable channels. Such channels have difficult access, and are used for laying one type of pipeline, for example supply and return heat pipes.
Channelless pipe laying
Laying pipes in the ground significantly reduces construction costs, reduces the amount of earthwork, and, accordingly, the construction time. The disadvantages of non-channel pipe laying include the complication of repair work, however, modern reinforced pipe shells can guarantee high reliability of such pipelines.
PVC pipe gasket
 Pipes made of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and chlorinated polyvinyl chloride are gradually replacing pipes and piping components made of steel and cast iron from the market. PVC pipes have a number of advantages that distinguish them from their iron counterparts:
Pipes made of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and chlorinated polyvinyl chloride are gradually replacing pipes and piping components made of steel and cast iron from the market. PVC pipes have a number of advantages that distinguish them from their iron counterparts:
- Light weight;
- Corrosion resistance;
- Low coefficient of linear thermal expansion;
- Neat look;
- Low cost;
- High resistance to chlorine and many other chemicals;
- Do not require welding, etc.
PVC pipes are successfully used not only in sewage and cold water pipelines, but also in hot and heat supply systems.
K-V-S LLC lays heating pipes made of PVC. Our experts will conduct pipe laying using the most modern equipment in the shortest possible time and at a high level, causing a minimum of inconvenience to the customer.
Source: http://www.k-v-s.ru/services/prokladka_trub_otopleniya/
Pipelines heating networks can be laid on the ground, in the ground and above the ground. With any method of installation of pipelines, it is necessary to ensure the greatest reliability of the heat supply system at the lowest capital and operating costs.
Capital expenditures determined by the cost of construction works and the cost of equipment and materials for laying the pipeline. IN operational include the costs of maintenance and maintenance of pipelines, as well as the costs associated with the loss of heat in the pipelines and energy consumption throughout the route. Capital costs are determined mainly by the cost of equipment and materials, and operating costs are determined by the cost of heat, electricity and repair.
The main types of pipeline laying are underground and aboveground. Underground piping is the most common. It is divided into laying pipelines directly in the ground (channelless) and in channels. With surface laying, pipelines can be located on the ground or above the ground at such a level that they would not impede the movement of vehicles. Overhead laying is used on suburban highways at the intersection of ravines, rivers, railways and other structures.
Overhead Gaskets pipelines in channels or trays located on the surface of the earth or partially buried, are used, as a rule, in areas with permafrost soils.
The method of installation of pipelines depends on the local conditions of the facility - purpose, aesthetic requirements, the presence of complex intersections with structures and communications, soil category - and should be taken on the basis of technical and economic calculations of possible options. Minimum capital expenditures are required for the installation of a heating main using underground pipe laying without isolation and channels. But significant losses of thermal energy, especially in moist soils, lead to significant additional costs and to premature failure of pipelines. In order to ensure the reliability of the heat pipes, it is necessary to apply mechanical and thermal protection.
Mechanical protection pipes during the installation of pipes underground can be provided by the installation of channels, and thermal protection - by confusing the use of thermal insulation applied directly to the outer surface of pipelines. The isolation of pipes and their laying in channels increases the initial cost of the heating main, but quickly pays off during operation by increasing operational reliability and reducing heat losses.
Underground piping.
When installing pipelines of heating networks underground, two methods can be used:
- Direct laying of pipes in the ground (channelless).
- Laying pipes in the channels (channel).
Laying pipelines in the channels.
In order to protect the heat pipe from external influences, and to ensure free thermal elongation of the pipes, channels are intended. Depending on the number of heat pipes laid in one direction, non-passage, semi-passage or passage channels are used.
To secure the pipeline, as well as to ensure free movement with temperature extensions, the pipes are laid on supports. To ensure the outflow of water, the trays are stacked with a slope of at least 0.002. Water from the lower points of the trays is removed by gravity into the drainage system or from special pits with a pump is pumped into the sewer.
In addition to the longitudinal slope of the trays, the floors should also have a transverse slope of the order of 1-2% for the removal of flood and atmospheric moisture. With a high level of groundwater, the outer surface of the walls, floors and the bottom of the channel are covered with waterproofing.
The depth of the laying of trays is taken from the condition of the minimum amount of earthwork and the uniform distribution of concentrated loads on the overlap when driving vehicles. The soil layer above the channel should be about 0.8-1.2 m and not less. 0.6 m in places where traffic is prohibited.
Impassable channels used with a large number of pipes of small diameter, as well as a two-pipe gasket for all diameters. Their design depends on soil moisture. In dry soils, block channels with concrete or brick walls or single or multi-cell reinforced concrete channels are most widely used.
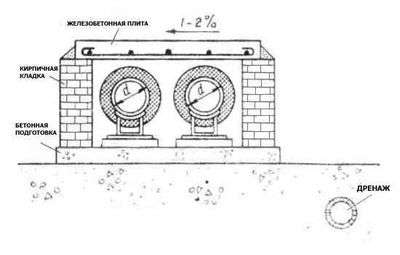
The walls of the channel can have a thickness of 1/2 brick (120 mm) for small diameter pipelines and 1 brick (250 mm) for large diameter pipelines.
The walls are erected only from ordinary brick of a brand not lower than 75. Silicate brick, because of its low frost resistance, is not recommended. The channels are blocked with reinforced concrete slab. Brick channels, depending on the category of soil, have several varieties. In dense and dry soils, the bottom of the channel does not require concrete preparation; it is good enough to ram the crushed stone directly into the soil. In soft soils, an additional reinforced concrete slab is laid on a concrete base. At a high level of standing groundwater, drainage is provided for their removal. Walls are erected after installation and insulation of pipelines.
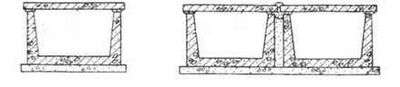
For pipelines of large diameters, channels are used that are assembled from standard reinforced concrete elements of the channel type KL and KLS, as well as from prefabricated reinforced concrete slabs KS.
KL-type channels consist of standard channel elements covered by flat reinforced concrete slabs.
KLs-type channels consist of two tray elements stacked on top of each other and connected on a cement mortar using an I-beam.
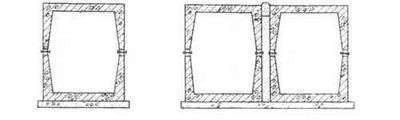
In KS type channels, wall panels are installed in the slots of the bottom plate and poured with concrete. These channels are covered with flat reinforced concrete slabs.
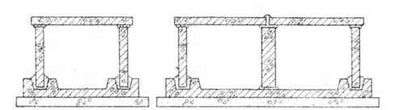
The bases of all types of canals are made of concrete slabs or sand preparation, depending on the type of soil.
Along with the channels discussed above, their other types are also used.
Vaulted channels consist of reinforced concrete arches or semicircular shells that cover the pipeline. At the bottom of the trench, only the base of the canal is made.
For large diameter pipelines, a vaulted two-cell channel with a dividing wall is used, while the channel arch is formed from two half-arches.
When installing an impassable channel intended for laying in wet and soft soils, the walls and bottom of the channel are made in the form of a reinforced concrete trough-shaped tray, and the overlap consists of prefabricated reinforced concrete slabs. The outer surface of the tray (walls and bottom) is covered with waterproofing from two layers of roofing material on bitumen mastic, the surface of the base is also covered with waterproofing, then the tray is installed or concrete. Before backfilling the trench, the waterproofing is protected with a special brick wall.
Replacement of pipes that fail, or repair of thermal insulation in such channels is possible only during the development of groups, and sometimes the dismantling of the bridge. Therefore, the heat network in impassable channels is traced along the lawns or in the green spaces.
Semi-passage channels. In difficult conditions, when heat pipes cross the existing underground devices (under the roadway, with a high level of groundwater standing), semi-passage channels are arranged instead of impassable ones. Semi-passage channels are also used with a small number of pipes in those places where, under the operating conditions, the opening of the carriageway is excluded. The height of the semi-bore channel is taken equal to 1400 mm. The channels are made of precast concrete elements. The designs of the semi-bore and bore channels are almost the same.
Feedthroughs used in the presence of a large number of pipes. They are laid under the bridges of large highways, in the territories of large industrial enterprises, in areas adjacent to the buildings of cogeneration plants. Along with the heat pipes, other underground communications are also located in the passageways - electric cables, telephone cables, water pipes, gas pipelines, etc. The collectors provide free access for service personnel to pipelines for inspection and liquidation of the accident.
The passage channels should have natural ventilation with a triple air exchange, providing an air temperature of not more than 40 ° C, and lighting. Entrances to the passage channels are arranged every 200 to 300 m. In places where stuffing boxes designed to absorb thermal extensions are located, locking devices and other equipment arrange special niches and additional hatches. The height of the passage channels must be at least 1800 mm.
Their designs come in three types - from ribbed plates, from links of a frame structure and from blocks.
Feedthroughs of ribbed plates. They are made of four reinforced concrete panels: the bottom, two walls and floor slabs, manufactured in the factory on rolling mills. The panels are bolted and the outer surface of the channel overlap is covered with insulation. Canal sections are mounted on a concrete slab. The weight of one section of such a channel with a cross section of 1.46 x 1.87 m and a length of 3.2 m is 5 tons, the entrances are arranged every 50 m.
The passage channel from reinforced concrete links of a frame design. top coated with insulation. Channel elements have a length of 1.8 and 2.4 m and are of normal and increased strength when buried, respectively, to 2 and 4 m above the ceiling. Reinforced concrete slab is placed only under the joints of the links.
The next type is a collector made of reinforced concrete blocks of three types: L-shaped wall, two floor slabs and the bottom. Blocks at the joints are connected by monolithic reinforced concrete. These collectors are also normal and reinforced.
Channelless gasket.
In case of channelless installation, protection of pipelines from mechanical influences is performed by reinforced thermal insulation - shell.
The advantages of channel-free pipelines are: the relatively low cost of construction and installation works, a decrease in the volume of earthwork and a reduction in construction time. Its disadvantages include: the complication of repair work and the difficulty of moving pipelines trapped in soil. Non-channel laying of pipelines is widely used in dry sandy soils. It finds application in wet soils, but with a mandatory device in the area of \u200b\u200bthe drainage pipes.
Movable supports for channelless piping are not used. Pipes with thermal insulation are laid directly on a sand cushion located on a pre-aligned bottom of the trench. The sand cushion, which is a bed for pipes, has the best elastic properties and allows the greatest uniformity of temperature movements. In weak and clay soils, the sand layer at the bottom of the trench should be at least 100-150 mm thick. Fixed supports for channelless pipe laying are reinforced concrete walls mounted perpendicular to the heat pipes.
Compensation of thermal displacements of pipes with any method of their channelless laying is ensured by bent or stuffing boxes installed in special niches or chambers.
At bends of the route, in order to avoid clamping the pipes in the ground and to ensure possible movements, impassable channels are arranged. At the intersection of the drip wall of the pipeline as a result of uneven precipitation of soil and the base of the channel, the greatest bending of the pipelines occurs. To avoid bending the pipe, it is necessary to leave a gap in the wall opening, filling it with elastic material (for example, an asbestos cord). Thermal insulation of the pipe includes an insulating layer of autoclaved concrete with a bulk weight of 400 kg / m3, which has steel reinforcement, a waterproofing coating consisting of three layers of brisol on bitumen-rubber mastic, which includes 5-7% rubber crumb and a protective layer made of asbestos-cement plaster on a steel mesh.
The return pipeworks are isolated in the same way as the feed pipes. However, the insulation of the return pipes depends on the diameter of the pipes. With pipe diameters up to 300 mm, an insulation device is required; with a pipe diameter of 300-500 mm, the insulation device should be determined by the technique of economic calculation based on local conditions; with a pipe diameter of 500 mm or more, an isolation device is not provided. Pipelines with such insulation are laid directly on the leveled compacted soil of the base of the trench.
To lower the groundwater level, special drainage pipelines are provided, which are laid at a depth of 400 mm from the bottom of the channel. Depending on the operating conditions, drainage devices can be made of various pipes: ceramic concrete and asbestos-cement ones are used for pressureless drains, and steel and cast-iron for pressure ones.
Drainage pipes are laid with a slope of 0.002-0.003. At bends and at differences in pipe levels, special inspection wells are arranged according to the type of sewer.
Overhead laying of pipelines.
Based on the convenience of installation and maintenance, laying pipes above the ground is more advantageous than laying underground. It also requires less material costs. However, this will affect the appearance of the environment and therefore this type of pipe laying may not be used everywhere.
Bearing structures for overhead piping serve: for small and medium diameters - above-ground supports and masts, ensuring the location of the pipes at the desired distance from the surface; for pipelines of large diameters, as a rule, support racks. Supports are usually made of reinforced concrete blocks. Masts and overpasses can be either steel or reinforced concrete. The distance between the supports and masts during overhead installation should be equal to the distance between the supports in the channels and depends on the diameters of the pipelines. In order to reduce the number of masts, intermediate supports are arranged using stretch marks.
When installing above ground, the thermal extensions of the pipelines are compensated by bent expansion joints, requiring minimal maintenance time. Rebar service is carried out from specially arranged sites. Rolling bearings should be used as moving ones, creating minimal horizontal forces.
Also, when installing pipelines above ground, low supports can be used, which can be made of metal or low concrete blocks. At the intersection of such a route with pedestrian paths, special bridges are installed. And at the intersection with highways - they either make a compensator of the required height or under the road lay a channel for the passage of pipes.
Previous material

Factory multilayer pipes
An article on how to insulate heating pipes on the street, indoors and when laying utilities underground. The types of heat insulators and methods of their application are considered.
Why do you need to insulate communications
Perhaps someone may wonder why to insulate what is already hot. Indeed, the heating circuit is always warm, since the heated coolant circulates in it. Do not forget that all heaters for heating pipes have excellent heat-insulating qualities.
The essence of warming heating pipes is that the coolant retains its temperature for as long as possible.
It is especially important to use insulation for heating pipes, if from the place of heating the water to the heated room the heating main passes through the air or underground. Suppose that the pipe is not insulated, for heating it is extremely negative. In this case, the boiler, or a set of heaters, raises the temperature of the water in the system and directs the working fluid to the place where it should give up its heat. Such places are heated residential and non-residential areas. The coolant interacts with the walls of the circuit and heats them. And those, in turn, interact with the environment. As a result, the water in the system becomes colder and, accordingly, the temperature in the heated room will also be lower.
It turns out that a certain amount of fuel was spent to heat the water. And since significant heat losses occur from the place of heating of the coolant to the destination point, the efficiency of the heater becomes lower. They burned a lot of fuel, and in heated rooms the temperature is not high. Therefore, to reduce fuel consumption and increase efficiency, it is necessary that the pipe is insulated. For heating in private homes and for large highways, various materials are used.
Varieties of heat insulators
Below are the main materials for thermal insulation of communications:

Thorough insulation of heating pipes
To warm the heating pipes on the street, special mineral wool is used. Minvata for heating pipes is of several types:
- Basalt - made from rocks with a high content of basalt. A feature of this insulation is its high resistance to heat, the operating temperature reaches 650 degrees Celsius. Basalt wool does not react with chemical compositions and does not emit toxic substances when heated.
- Fiberglass - The main component is quartz sand. It is used not only in its pure form. Glass is made from sand, which is also part of this insulation. This material can only be used for insulation of external pipes, since the temperature of their operation is less than two hundred degrees, about 180.
The disadvantage of such insulation of heating pipes is the tendency of the material to absorb moisture, which negates all its heat-insulating characteristics. How to insulate heating pipes on the street to avoid getting mineral wool wet? It is for this purpose that waterproofing is used in tandem with basalt or glass wool.
It should exclude contact of the insulation with moisture, since the insulation of heating pipes on the street is possible due to the porous structure of the cotton wool. And when water fills the air cavity, the temperature of the coolant through the best conductor, water, is transmitted to the air. Therefore, it is important to protect the insulation layer from moisture.
The easiest way is to wrap the insulated trunk with roofing material, which can be fixed with wire. Cheap and cheerful, but the method is proven by many years of practice. At the same time, any waterproof material with sufficient resistance to mechanical stress can be used as waterproofing;

For communications, special shapes are made that repeat their geometry. Usually, this is a two-part ring. In each part there is a groove joint, which creates an additional barrier to moisture.
Polyfoam almost does not absorb moisture and this can cause problems, since heating pipes in the ground must be insulated with absolutely moisture-proof materials.
Although there is a special type of polystyrene foam called extrusion. It is denser than regular polystyrene foam and completely waterproof.
Polyurethane foam can also be attributed to this group of heaters. They are similar in composition. Such materials can be both individual elements of insulation, and parts of a single design of a multilayer pipe for heating. It is also possible to apply the aforementioned formulations in liquid form. For this, special compressors are used, with the help of which the heater is sprayed onto the working surface. In this case, the advantage is the complete tightness of the insulation layer;
- foamed insulation for heating pipes.
These are products in the form of a cover. As the material used: rubber, polystyrene foam or polyurethane. Their inner diameter coincides with the standard dimensions of the heating circuits. In order to wear such a cover, a longitudinal section is provided, which is then glued. To do this, a special adhesive is applied to the end of the cut;
- reflective winding of heating pipes.

Penofol - reflective insulation
The name speaks for itself. The bottom line is the reflection of warm currents due to the mirror surface of the insulation. To do this, use aluminum foil. It is wound on top of the main insulation and fixed with a metal wire, or clamps. Insulators for heating pipes with foil simultaneously perform several functions:
- reflects warm currents back to the circuit;
- does not let cold outside;
- protects from wind and moisture.
Also, the foil is used in tandem with foamed polyethylene or polyurethane. For example, penofol, which consists of a synthetic layer of foamed insulation and a layer of foil glued to it. It is produced in rolls of different widths and is used not only to isolate communications, but also to create a “thermos” effect when warming rooms;
A fairly new type of insulation. It was first used for space modules. The designers were faced with the task of creating an effective heat insulator with minimum weight, since when launching spacecraft and satellites, every gram matters. A few millimeters of such paint is enough to replace a thicker layer of other heaters. It is widely used for warming heating mains.
Indoor insulation
Of course, insulation of heating pipes in a house where the coolant must give up its heat is not necessary. But when it comes to unheated rooms, then the insulation of heating pipes with your own hands is very important. These include basements and attics. There is no water in the basement and should not be. The insulating layer can be threatened only by increased humidity, which is insignificant for materials such as basalt wool, polystyrene foam and polyurethane. To warm the heating pipes in the basement, any of the above materials will do, even without the use of additional waterproofing.
Most often, for domestic purposes, use covers made of expanded polystyrene foam, popularly referred to as "gray skin". But because of their high cost, they are often inferior to a cheaper type of insulation - mineral wool. In private houses with open heating, some circuit elements are located above the ceiling of the heated room. It is very important to provide for the insulation of pipes and a heating tank in the attic. The location of the latter is explained by the need to place it at the peak point of the contour.
Before insulating heating pipes in the attic, thoroughly familiarize yourself with the characteristics of the material. It must be resistant to heat. In the tank, the coolant temperature sometimes reaches a boiling point.
Underground insulation

Such pipes are laid underground
Heating pipes are laid underground. Important points when warming heating pipes in the ground:
- to bury communications below the freezing level. For each region, this indicator is individual;
- prevent moisture from entering the insulation;
- prevent deformation of the insulation layer under the weight of the earth.
Laying communications underground has always been expensive, since special attention is required to warming.
The most common method is the use of heaters in conjunction with hard casings. It could be:
- Communications wrapped with insulation, which are placed in plastic sewer pipes, with a diameter of 110 or 160 mm. Mineral wool, foamed materials or polystyrene can act as a heater for heating pipes in the ground.
- Factory multilayer pipes.
The latter come in various configurations. The main thing that unites them is a pipe (plastic or metal), a layer of insulation and a rigid frame. The high cost of such products often becomes the reason for warming heating pipes underground in the first way.
Insulation on the street
In order to insulate heating pipes on the street, it is necessary to take into account the possibility of contact with moisture. It can be rain or snow. Therefore, mandatory waterproofing should be provided. The standard way to heat the heating pipes on the street:
- layer of mineral wool;
- winding with silk threads;
- layer of roofing material;
- winding of corrosion resistant metal wire (galvanized or aluminum).
Do heating pipes need to be insulated? You probably have often seen the deplorable state of the insulating layer of heating mains in your city. This directly affects the temperature in the apartments. For example, there is a temperature level of the supplied coolant defined by state acts. Based on this value, the average temperature in residential premises and the cost of utilities are calculated.
Calculations are made taking into account the serviceability of all elements of the heating system, including the insulating layer of heating pipes passing from boiler rooms to houses. With insufficient thermal insulation in apartments, the temperature will be lower. It turns out that according to the documents everything is ranked, but in fact, the standard is not implemented and, as always, there are no guilty parties. And people at the same time should pay in full, although at home far from Tashkent.
Long gone are the days when residents of private houses and cottages ran for water to wells. Today, most summer residents have a laid water supply on the site, which allows you to relax in the lap of nature with maximum comfort.
Undoubtedly, if the water supply system is used only in summer, then the pipes can only be lightly sprinkled with earth. But what if you use the plumbing system all year round? How to insulate a water pipe underground? The experience of past generations has shown that even at -7 ° C, pipes at a shallow depth will completely freeze in a week!
Insulation materials
Most often, insulation of water pipes in the ground is carried out by the following materials:
- Polystyrene (polystyrene). Affordable, convenient and most importantly cheap material, the installation of which does not require a professional approach. Even underground, the foam retains all its properties and can be reused, for example, after pipe repair;
- Perfect DIY material. This insulation is a cylinder made of basalt fiber and coated with a protective layer of roofing material. With the help of special fasteners, a snug fit to the pipe is ensured. But there is one significant minus - the high price of a product is not always affordable for an ordinary citizen;
Attention! The heat-insulating material must have inherent qualities and characteristics that are approved not only by the manufacturer, but also by GOST.
When choosing and buying heat-insulating materials for pipes, you should pay attention to the following factors:
- Resistance of a heater to aggressive environmental influences;
- Water absorption;
- Low thermal conductivity and high rates of heat conservation;
- The ability to withstand operating temperatures without additional insulation.
In general, for a heater there are several basic criteria:
- tightness;
- fire safety;
- durability;
- ease of installation.
It is thanks to these indicators that you can safely enjoy a vacation in the country or live quietly, forgetting about pipes, a dozen or two years longer.
Proper insulation
So, let's start with the fact that the insulation of water pipes in the earth with glass wool is most often done in cottages. First, pipes are wrapped with this material and then fixed with a special tape. Further, with the help of roofing material or other waterproofing materials, they provide protection against moisture.
As for the foam or basalt insulation, or as it is also called "shells", then everything is simple. Their halves are worn on one side of the pipe, with a slight displacement relative to each other. Then, the halves are fastened with adhesive tape, which is glued with a special waterproof glue for reliability. The next layer is protective material.
In order to warm the water pipe in the ground, taking into account the closure of all turns and corners, shaped shells are used. The diameter of the shell should be selected so that the insulation is closely adjacent to the pipes.
Pressure or heating cable: add heat
As you know, water under constant strong pressure does not freeze. A definite conclusion should be drawn from this - the heating cable will prevent the freezing of water in the pipes. To implement this method, it will be enough to install the receiver. Also, to maintain a constant pressure throughout the water supply line (from the pump to the receiver), a check valve must be connected to the pump. Then close the tap in front of the receiver and start the pump.
When you decide to leave the cottage or cottage for an indefinite time, you must turn on the pump and thereby create a working pressure of at least 3-5 atmospheres (depending on the capacity of the pump). Under such conditions, you can not be afraid that the water in your water system will freeze.
If you want to insulate the water supply with a heating cable, then perhaps you will do right choice. Why? Because it is the most reliable way to heat underground utilities. Due to the fact that pipes (even buried to a depth of 2 meters or more) can only thaw on their own by May, using a heating cable you can heat them in one day.
When using this method of heating, it is not necessary to deepen the pipes into the soil by 2 meters - in the presence of a heating cable, the depth of the trench can not exceed 50 centimeters. With an average step of 10-15 cm, the pipe is wrapped with a cable whose power is 10-12 watts per 1 m. Its location will not affect the system's performance in any way - whether it is inside the pipe or wound outside.
About "width \u003d" 640 ″ allowfullscreen \u003d "" frameborder \u003d "0 ″\u003e

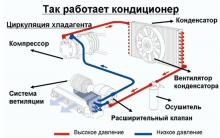
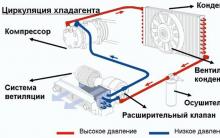






The best material for car trim
Principles of hardening the body
Do-it-yourself compressor - with minimal scrap costs
Which is better: do-it-yourself or factory-made compressor for painting a car
Causes of fuel pump malfunctions