It is well known that feathers protect the body of a bird, wool for animals, and hair grows on the human body. They are absent only on the palms and feet. The body hair is a kind of atavism, inherited from time immemorial to man. On the body of an adult, there are from 300 to 500 thousand hairs. Blond people have the most body hair and redheads least of all, with red hair being the toughest to the touch.
The growth of hair on the body of an adult largely depends on the work of the sex glands. Male hormones increase the development of facial and body hair and inhibit hair growth on the scalp. Female hormones, on the other hand, promote the development of hair on the head, but not on the body or face.
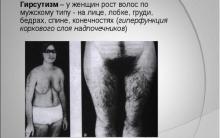
In medicine, there are two concepts that describe excess hair growth - hirsutism and hypertrichosis. Hirsutism- Excessive growth of terminal (coarse, coarse) hair in women according to the male pattern. Terminal hair is dark, coarse, long, in contrast to vellus hair, which is poorly colored, soft and short. It is only about the appearance of hair on the chin, upper chest, upper back and abdomen. Terminal hairs in the lower abdomen, lower back, near the nipples, arms and legs are normal. The condition is not synonymous with virilism, in which women, in addition to manifestations of hirsutism, develop secondary male sexual characteristics.
Hypertrichosisunlike hirsutism, it is characterized by excessive hair growth in places where it is the norm, and can be observed in both sexes. Men do not suffer from this, but for young ladies this problem brings a lot of trouble and causes psychological discomfort up to the appearance of an inferiority complex.
Distinguish between congenital and acquired forms of hypertrichosis. The congenital form of general hypertrichosis, in which the entire surface of the skin is covered with long wavy hair, is a very rare anomaly that progresses to puberty. In congenital limited hypertrichosis, excess hair grows on pigmented skin, often in the sacrum. The congenital general form of hypertrichosis cannot be treated. With a limited form, surgical intervention is sometimes possible.
The acquired form of hypertrichosis can occur in places of prolonged skin irritation (rubbing in ointments, plaster bandages), in patients with tuberculosis, osteomyelitis. Sometimes in girls in puberty (puberty) or in women in menopause, increased hair growth begins on the face, above the upper lip.
Increased hair growth in areas where it is undesirable is not only a cosmetic defect. The appearance of a beard and mustache in women can be a symptom of various diseases.
Most often, endocrine hypertrichosis associated with diseases of the ovaries and a violation of their hormonal function, damage to the adrenal cortex are observed. Less commonly, tumors of the anterior pituitary gland can be the cause of increased hair growth.
Often, hypertrichosis occurs during pregnancy as a result of increased hormonal activity of the endocrine organs of the brain (anterior pituitary gland). Increased growth of facial hair in the cheekbones and temples can be a manifestation of metabolic disorders.
Therefore, starting the process of getting rid of excess hairs, it is necessary to consult with a gynecologist, endocrinologist, neuropathologist about the possible reason for their appearance, so that, together with the solution of the aesthetic problem, it is also possible to find an internal defect, and a complex effect on the cause will help to achieve faster desired results.
Recently, there has been an increase in drug hypertrichosis caused by the intake of medications such as corticosteroid drugs, anabolic steroids. Long-term treatment with male sex hormones also leads to the growth of coarse dark facial hair.
Incorrectly selected creams (especially based on lanolin), with prolonged use, increase hair growth above the upper lip and on the chin. Therefore, it is not recommended to apply nourishing creams, especially those containing hormonal and biostimulating substances, to the lower third of the face, since they improve the nutrition of the skin, including the hair follicles.
Thermal cosmetic procedures, as well as irritating resorbable masks, enhance microcirculation, improve blood flow to the hair follicles and thus promote the growth of excess hair. Therefore, the presence of hypertrichosis on the face is a contraindication for the use of infrared thermal radiation, quartz, sunbathing, paraffin masks, body masks and the like.
Sometimes women themselves unknowingly contribute to the fact that colorless vellus hair becomes coarse and dark. This usually happens as a result of shaving them off or pulling them out with tweezers.
So why does facial hair grow?
- Violation of the hormonal background, or rather the presence of an increased level of male hormones - testosterone. This trouble is primarily of a medical nature, since the ovaries and adrenal glands are malfunctioning. To exclude such causes of facial hair, you should first of all contact an endocrinologist.
- Heredity, genetic abnormalities. Some peoples of the world, most often Caucasian and southern, women have a small facial hair. Hereditary causes of unwanted hair do not require special treatment, and the aesthetic problem can be easily solved by laser hair removal, which is the safest and most effective method.
- Chronic stress
- Improper diet entails not only obesity, but also excess hair
- With menopause, hair also appears on the face. All these problems are closely related to hormonal changes in women in adulthood.
- Unwanted facial hair can also appear during puberty or pregnancy.
- Facial hair in girls can be the result of long-term use of birth control pills.
- Complications of diseases. For example, brain tumor, kidney pathology, epilepsy.
- Environmental issues can also lead to excess facial hair.
- The use of certain drugs, especially those containing prednisone, cortisone, hydrocortisone - corticosteroids.
In modern times, a perfectly smooth body is appreciated, excluding the hair on the head. Excessive hair growth on the body of women has recently become widespread. This pathology has a name - when hair growth occurs in the back, chest, face and stomach.
And there are also a number of reasons for the appearance of excess body hair. Such unwanted vegetation primarily causes aesthetic discomfort. The causes of facial hair growth in women can be a serious call that a malfunction has occurred in the body, and indicate serious disorders that should be diagnosed and treated.
Hirsutism, what is it?
Many of us have seen women who grow a man's beard or mustache. The reasons for chin hair growth in women can be very different. One of these pathologies is called hirsutism - a female diagnosis, which means excess hair growth in the fair sex with an excess of male hormone.

Such a disease brings many aesthetic inconveniences to the life of women, and also forms complexes. Indeed, for men, women with an overabundance of hair, especially on the face, become unattractive. Such hair has a different type of hair follicles and grows coarse, dark, long.
1 in 20 women of childbearing age develop facial hair. And after 50 years, every fourth. However, the disease hirsutism is often accompanied with serious consequences: menstrual irregularities, inability to conceive a child, depression.
The reason for the appearance of hirsutism is an increased level of testosterone (male sex hormone) in a woman's body. Such an increase may appear due to a malfunction of the ovaries. Among women, the disease is common -. The ovaries produce the following hormones:
- estrogens;
- gestagens;
- androgens.

If the amount of androgens increases sharply, then the body experiences stress and triggers the following reactions:
- a sharp increase in facial hair;
- enlargement of the genitals;
- increase in muscle mass;
- hoarseness change of voice.
Hirsutism can be a consequence of the following processes:
- taking hormonal drugs;
- pathology of the adrenal glands;
- oncological pathologies;

- pathology in the functioning of the pituitary gland;
- metabolic pathology;
- genetic predisposition;
- puberty, menopause, pregnancy.
In addition to increased body hair growth, the following symptoms are possible:
- baldness;
- violation of the menstrual cycle;
- infertility;
- increased oily hair;
- increase in muscle mass;
- increased sex drive.

Hypertrichosis, what is it?
The cause of excess body hair growth in women can be a disease -. This pathology includes such symptoms - excessive hair growth in any part of the body. Most often, the pathology is observed in Asian women.
The reasons for the appearance of hirsutism and hypertrichosis are the same and are associated with an excess of testosterone:
- ovarian dysfunction is the most common cause of hair growth;
- adrenal gland diseases;
- pathology in the work of the pituitary gland;
- increased production of androgens;

- metabolic disease;
- oncology;
- skin pathologies;
- genetic mutations;
- against the background of hormonal changes (menopause, pregnancy, puberty);
- anorexia nervosa.
The disease can be congenital and acquired. Hair growth does not necessarily cover any part of the body evenly. They can grow unevenly, in atypical places, for example, on the shoulder or shoulder blade, etc. This distinguishes the two diseases presented above.
With Hypertrichosis, vellus hair grows, covering almost the entire body, pigmented in some places. Each part of hair growth has its own reasons, which are important to diagnose in a timely manner and start treatment.

Other reasons
The reason for a sharp increase in hair can be stress. When a girl is engaged in difficult work, the body and psyche begin to rebuild to produce testosterone. In medicine, there is such a thing as masculinization of a woman.
And also sudden hair growth can occur due to the following reasons:
- nervous exhaustion;
- depression;
- anorexia;
- pathology of the nervous system.
Due to trauma to moles, due to frequent hair removal.
Often, vegetation increases in women by the age of 50, when age-related changes and natural attenuation of the ovaries occur.
Diagnosis of pathology
An increased increase in facial hair growth and chest hair growth in women may be a cause for concern. You should consult a doctor for the correct diagnosis and search for the cause of increased male pattern hair.
Diagnostics includes consultations and examination by a gynecologist, endocrinologist, taking anamnesis, laboratory tests.
An instrumental examination is mandatory:
- Ultrasound of the ovaries and adrenal glands;
- MRI and CT of the brain;
- ovarian laparoscopy if a tumor is suspected.
And also it is worth contacting a neurologist, trichologist and cosmetologist.

Treatment of increased body hair growth
When the cause of the excess hair growth has been identified, treatment can begin. Usually, the treatment of excess hair growth consists of the following steps:
- the use of drugs that lead to a decrease in testosterone;
- elimination and treatment of the primary cause of the onset of the disease;
- correction of diet and special diet;
- hair removal by cosmetic methods.
If hair growth is not associated with some kind of disease, then appoint:
- antiandrogenic drugs: Janine, Cyproterone, Ketoconazole, Diane-5;
- drugs that contain progestogen and estrogen.

Drug therapy
Mandatory treatment for hirsutism and hypertrichosis is hormonal therapy. Oral contraceptives, which suppress male hormones in the ovaries. The following drugs are considered effective:
- Finasteride;
- Matformin;
- Spironolactone.
Hormone therapy slows down the growth of new hairs. It can only be prescribed with the complete exclusion of tumors. It is mandatory to take drugs that reduce testosterone levels and sensitivity to androgens: Dine-35, Janine, Yarina.
For adrenal pathology, appoint: Cortisol, Prednisolone. And if a tumor of the ovaries or adrenal glands is diagnosed, the doctor may prescribe chemotherapy. Treatment with hormones lasts about six months.
Contraindications to treatment with hormonal drugs: pregnancy; lactation; tumors; allergic reactions to drugs.
When a woman is planning a child, hormonal agents are prohibited. However, the expectant mother often needs to stimulate ovulation. If you cannot conceive a child, then you can use IVF services.

Cosmetic treatment
After or during the period of hormonal treatment, you can begin to remove the hair. Do not shave coarse hairs with a razor or pluck them with tweezers. Especially if they grow on the face. Therefore, along with hormonal therapy, cosmetic therapy should be included in order to bring the body back to normal.
There are the following types of cosmetic hair removal:
- photoepilation - due to the effect of high-pulse light, the tissues are heated, the hair follicles are destroyed;
- laser hair removal is an unpleasant, expensive, but effective procedure. With the help of a laser, the follicle is destroyed and the hair is no longer disturbed;
- electrolysis - with the help of a current, hair follicles are removed;
- a mixture of electrolysis and photoepilation - new, removes hair of all skin types;
- waxing - short-term hair removal for a month maximum;
- shugaring - hair removal with a sugar solution.

Folk methods
At home, you can independently carry out cosmetic procedures and try to minimize the visibility of excess hair. Sugar hair removal is easy to do yourself:
- mix one glass of sugar with three tablespoons of water and a pinch of citric acid;
- heat the mixture over a fire until a homogeneous mass is slightly brownish;
- when the mixture cools a little, pick up the paste and apply to the area with excessive cover;
- remove hairs against growth.
It is worth minimizing the visibility of dark hair using folk recipes:
- take hydrogen peroxide or light hair dye. Apply with a sponge or cotton pad to hairs and hold for a few minutes. Repeat the procedure as needed;
- mix a teaspoon of baking soda with a tablespoon of boiling water and apply to the hairs. Keep the compress overnight;
- mix ash with soap (pre-rub) and dilute with a spoonful of water. Soak cotton wool and hold the compress for fifteen minutes;
- one spoonful of castor or burdock oil, two tablespoons of alcohol, a teaspoon of ammonia, five drops of iodine 5%. Treat the bikini area with the mixture twice a day.

If there is a likelihood of hereditary diseases in which a woman grows hair according to the male type, then it is better to pre-perform preventive actions:
- diet - control weight;
- visiting a beautician to remove follicles or bulbs;
- annual examination of all organs;
- choice of a female profession with minimization of stress.

It's important to know:
- the use of various medicines removes one problem and creates others;
- hormonal drugs are best used in extreme cases. Since hormones are removed from the body for several years;
- many medications disrupt the work of the gastrointestinal tract;
- taking hormonal drugs affects mood not for the better.
Facial hair growth is an unpleasant manifestation of hormonal imbalance. With the right foundation, and the development of therapy, it is treated in several stages.
- This is an overgrowth of stem hair in women, caused by male sex hormones - androgens.
There are two types of hair in humans: vellus and shaft hair. Cannon hairgrow from one type of hair follicles. By its structure, vellus hair is delicate, thin and short. Rod hair they germinate from another type of hair follicles. This type of hair is pigmented, the hairs are coarse, coarse, thicker. Under the influence of male sex hormones, hair follicles (follicles) of the first type can turn into bulbs of the second type, and, accordingly, hard hair of the rod type will grow from them.
Where does core hair grow normally in women?
Where in adult normal women does core hair grow on the body? First of all, such core hair is present on the scalp and eyebrows. Associated with the action of androgens, such hair grows in the armpits and on the pubis. The growth of stem hair on the legs and forearms is considered to be unrelated to the effects of male sex hormones. The growth of stem hair in the rest of the body can be regarded as hirsutism.The difference between hirsutism and hypertrichosis (excessive hair growth)
It should be noted that hirsutism must be distinguished from excessive body hair ( hypertrichosis). Hypertrichosis in contrast to hirsutism, it is characterized by increased growth of vellus hair. This growth of vellus hair is not associated with the action of androgens and may be the result of various metabolic and endocrine disorders (for example, with insufficient thyroid function), taking certain medications (minoxidil and others), and, finally, hereditary and constitutional features. The exception is the so-called idiopathic hirsutism, which has no connection with hormonal imbalance. It must be said that slight hair growth on the upper lip, around the nipples, along the midline of the abdomen from the pubis to the navel or just above the navel, is often observed in endocrinologically healthy women.The relationship between hirsutism and hyperandrogenism (increased levels of male sex hormones in the blood)
Hirsutism is one of the most persistent and often one of the earliest symptoms of hyperandrogenism.
Hyperandrogenism - This is a condition of the body in which there is an increase in the concentration of male sex hormones (androgens). That is, the concept of hirsutism is closely related to the concept of hyperandrogenism. Hyperandrogenism is the result of significant disturbances in the complex system of regulation of sexual function, which includes the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, ovaries and adrenal glands.
What can hyperandrogenism lead to?
 This condition is usually accompanied by a number of consequences and complications, among which, in addition to hirsutism, there are menstrual irregularities, metabolic disorders, miscarriage, and quite often - infertility. The most common reason for the lack of ovulation in infertile women is hyperandrogenism. Depending on the age at which the factors leading to hyperandrogenism begin to act, various clinical manifestations of the disease develop. These manifestations range from disturbance and lengthening of the second phase of the menstrual cycle to chronic absence of ovulation in combination with hirsutism, all kinds of metabolic disorders, miscarriage and infertility. In addition to violations of the sexual and reproductive functions, hyperandrogenism can lead to the development of pathologies of various, non-genital, organs. This condition significantly increases the risk of developing cancer of the mammary glands, the lining of the uterus (endometrium), diabetes mellitus, arterial hypertension, myocardial infarction.
This condition is usually accompanied by a number of consequences and complications, among which, in addition to hirsutism, there are menstrual irregularities, metabolic disorders, miscarriage, and quite often - infertility. The most common reason for the lack of ovulation in infertile women is hyperandrogenism. Depending on the age at which the factors leading to hyperandrogenism begin to act, various clinical manifestations of the disease develop. These manifestations range from disturbance and lengthening of the second phase of the menstrual cycle to chronic absence of ovulation in combination with hirsutism, all kinds of metabolic disorders, miscarriage and infertility. In addition to violations of the sexual and reproductive functions, hyperandrogenism can lead to the development of pathologies of various, non-genital, organs. This condition significantly increases the risk of developing cancer of the mammary glands, the lining of the uterus (endometrium), diabetes mellitus, arterial hypertension, myocardial infarction. How widespread is hirsutism?
Among the adult population, the incidence of hirsutism is 25-30% (with the exception of Asians and residents of northern countries). Hirsutism is not always associated with androgenism. However, the presence of hair growth on the back, shoulders, chest and upper abdomen may indicate that in this case, hirsutism is accompanied by hyperandrogenism.
The main causes of facial hair in women
The main cause is hormonesSince the increased growth of body hair is often accompanied by other changes in the skin, namely, an increase in its oil content, as well as the appearance of acne, acne and seborrhea, women often seek help from a dermatologist or cosmetologist. The described skin manifestations are regarded by these specialists as hyperandrogenic dermatopathy... Nevertheless, many studies show that patients with hyperandrogenism are treated for a long time and, often without effect, by therapists, dermatologists, endocrinologists, gynecologists, pediatricians and neuropathologists. What is the reason for this state of affairs? It's all about a very wide variety of clinical manifestations of the disease.
Types of hormones that cause facial hair in women The fact is that determining the source of increased androgen production is rather difficult. The situation is complicated by the fact that androgens in the female body are produced by both the ovaries and the adrenal glands. And hormones produced by the ovaries and adrenal glands have similar clinical effects.
The fact is that determining the source of increased androgen production is rather difficult. The situation is complicated by the fact that androgens in the female body are produced by both the ovaries and the adrenal glands. And hormones produced by the ovaries and adrenal glands have similar clinical effects.
What organs and in what diseases is an excess of hormones formed in hirsutism?
Why does such a malfunction occur and the ovaries or adrenal glands begin to produce androgens in an increased amount? In other words, what are the main causes of hyperandrogenism? There is a so-called adrenal androgeny and ovarian.
- - due to increased synthesis of androgens by the adrenal cortex, which occurs in congenital adrenal hyperplasia. This state of adrenal hyperplasia is observed in the following pathologies:
- congenital adrenogenital syndrome
- premature puberty
- congenital dysfunction of the adrenal cortex
- hormone-producing tumors of the adrenal cortex
- Ovarian hyperandrogenism - due to increased production of androgens in various types of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), as well as the synthesis of androgens by hormone-active ovarian tumors.
 In addition to ovarian and adrenal androgenism, there are two more types of this pathological condition, which are also associated with increased production of androgens. However, the increase in synthetic activity is not due to direct damage to the ovaries or adrenal glands. These types of hyperandrogenism include the following:
In addition to ovarian and adrenal androgenism, there are two more types of this pathological condition, which are also associated with increased production of androgens. However, the increase in synthetic activity is not due to direct damage to the ovaries or adrenal glands. These types of hyperandrogenism include the following: - Overproduction of androgens caused by damage to various central levels of regulation of the reproductive system. These central regulators of the reproductive system, localized in the brain, include the hypothalamic-pituitary system. Due to damage to the hypothalamic-pituitary system, such pathological conditions develop as: Itsenko-Cushing's disease, Morgagni-Stewart-Morel syndrome and others.
- Hyperandrogenism caused by a violation of the exchange of male sex hormones in peripheral tissues (skin), as well as a violation of the receptor interaction "androgen - hormone receptor" in the skin.
What are steroid hormones? Where and from what are steroids synthesized?
 For a better understanding of the processes occurring in the body with an excess of androgens, let us consider the general concepts of what androgens are, the mechanism and places of their synthesis, as well as the biological effects of male sex hormones.
For a better understanding of the processes occurring in the body with an excess of androgens, let us consider the general concepts of what androgens are, the mechanism and places of their synthesis, as well as the biological effects of male sex hormones. Androgens are steroid hormones. In addition to androgens, steroid hormones include estrogens and corticosteroids (adrenal hormones). The main representatives of androgens are testosterone and androstenedione. The testes, ovaries and adrenal glands produce steroid hormones. These glands have a common embryonic origin. Subsequently, during embryonic development during pregnancy and difficult stages of development, each of these glands (testes, ovaries, adrenal glands) begins to specialize in the predominant synthesis of one of the types of steroid hormones - estrogens, androgens or corticosteroids. Estrogens and androgens are synthesized from the precursor cholesterol common to all steroid hormones.
The entire process of the formation of each steroid hormone in the whole synthesis chain is controlled by a strictly defined set of enzymes. Due to this control, differences in the form of a synthesized steroid, which predominate in the ovaries, testes, adrenal glands, begin to appear already at the stage of development of the gonads (testicles and ovaries) and adrenal glands during embryonic development in the womb.
Both the ovaries and the adrenal glands, as well as peripheral tissues, contribute to the production of male sex hormones by producing androgens in various quantitative proportions.
Where and how are androgens formed in ovaries?
 Mainly, the process of androgen synthesis occurs in the stromal tissue of the ovary, and in the cells of the tecal membrane of follicles at certain stages of follicle development. Androgens are formed from progesterone, followed by transformation into cholesterol. From the androgens themselves, estrogens are synthesized, which enhance the growth of the follicle, and lead to the formation of a dominant follicle. The importance of androgen synthesis by the stromal component of the ovary is especially well manifested during the period of extinction of menstrual function, when the so-called "cellular" component of the ovaries decreases - a set of follicles at different stages of their development.
Mainly, the process of androgen synthesis occurs in the stromal tissue of the ovary, and in the cells of the tecal membrane of follicles at certain stages of follicle development. Androgens are formed from progesterone, followed by transformation into cholesterol. From the androgens themselves, estrogens are synthesized, which enhance the growth of the follicle, and lead to the formation of a dominant follicle. The importance of androgen synthesis by the stromal component of the ovary is especially well manifested during the period of extinction of menstrual function, when the so-called "cellular" component of the ovaries decreases - a set of follicles at different stages of their development. With hyperplasia of the ovarian stroma or the occurrence of a hormone-forming tumor, testosterone begins to be synthesized in increased quantities.
Where and how are androgens formed in the adrenal glands?
The main adrenal androgens are dehydroepiandrosterone and dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate. Adrenal androgens begin to form in the adrenal glands of the fetus during intrauterine development. The site of androgen synthesis is the reticular zone of the adrenal cortex. If before puberty the indicated zone is poorly developed, then in the period from 5 to 10 years, its intensive development takes place with the production of androgens and the manifestation of secondary sexual characteristics (hair growth in the armpits and pubis).What are the effects of androgens on peripheral tissues?
 Hormones exert their influence in those places where there are receptors for them. Receptors for androgens are present in the structures of the central nervous system, the male reproductive tract, bones, muscles, sebaceous glands of the skin, hair follicles and the mammary gland.
Hormones exert their influence in those places where there are receptors for them. Receptors for androgens are present in the structures of the central nervous system, the male reproductive tract, bones, muscles, sebaceous glands of the skin, hair follicles and the mammary gland. It is believed that testosterone, together with estrogens at the level of the central nervous system, influences the sex drive (libido). On the mammary gland, androgens have an effect opposite to that of estrogens, as a result of which the gland tissue does not develop enough. This picture is observed in women who had an excess of androgens at the beginning of puberty (for example, with hyperplasia of the adrenal cortex).
The influence of androgens leads to an increase in muscle mass, growth of tubular bones in length, and an increase in bone density.
The target of androgens in women is the skin. As a result of exposure to hair follicles localized on the face and body, delicate vellus hair turns into coarse and coarse, pigmented hair.
As mentioned above, hyperandrogenism is not an independent disease. It is part of a complex of metabolic metabolic disorders, which is inherent in a particular pathological condition. And hirsutism, we repeat, is the most characteristic manifestation of increased production of androgens.
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) as a cause of hirsutism
 The frequency of occurrence of polycystic ovaries. Clinical symptoms of polycystic ovary syndrome. Stein-Leventhal syndrome triad
The frequency of occurrence of polycystic ovaries. Clinical symptoms of polycystic ovary syndrome. Stein-Leventhal syndrome triadConsider the increased production of androgens by the ovaries, since this pathological condition occurs in the population most often compared to other hyperandrogenic syndromes.
The classic manifestation of this pathological condition is polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). This pathology is quite common in gynecological practice, mostly in women with infertility and menstrual irregularities. Attention was drawn to the phenomenon of the so-called "cystic ovarian degeneration" as early as 1845. Also at the end of the 19th century, the operation of wedge-shaped resection or removal of the ovaries was proposed to reduce the level of androgens produced by them. In 1935, a triad of symptoms was described that included obesity, polycystic ovaries, and no ovulation. This triad is called Stein-Leventhal syndrome. The frequency of this syndrome among women of fertile age is 3-11%, and among patients with infertility - 18-20%. In women suffering from various menstrual irregularities and hirsutism, polycystic ovary syndrome is detected in more than 60% of cases.
Causes and mechanism of development of polycystic ovary syndrome
This syndrome is based on the primary lesion of the central structures (hypothalamic-pituitary system) that regulate menstrual function. A connection was revealed between the onset of the disease and the onset of sexual activity, change of place of residence, physical and mental overload, childbirth, abortion, various intoxications - that is, various stressors. Violation of the central regulatory mechanisms can occur due to acute or chronic infection, poisoning in the periods before and during puberty.Of great importance is the increased level of androgen secretion several years before the onset of the first menstruation (menarche). The excess androgens of the adrenal glands are converted to estrogens, and their increased level eventually stimulates the increased production of androgens in the ovaries, the overproduction of which becomes self-sustaining. That is, the so-called vicious circle is closed.
The onset of the disease, as a rule, coincides with the onset of menstrual function (menarche) or in the near future. Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) reveals polycystic changes in the ovaries in the overwhelming majority of patients with similar disorders in the sexual function regulation system. On the other hand, many authors attach great importance in the occurrence of cystic changes in the ovaries to disorders of fat metabolism (obesity), since androgens are transformed into estrogens in adipose tissue. And an excess of estrogens produced on the periphery leads to a violation of the hormone-producing function of the ovaries. Additional factors in the development of polycystic ovary syndrome are: increased insulin production and insulin resistance. This means that a significant increase in the amount of androgens occurs during a glucose exercise test. An important role in the development of polycystic ovary syndrome is also assigned to defects in specific enzyme systems that ensure the normal synthesis of steroid hormones.
With such types of endocrine pathology as, for example, a decreased function of the thyroid gland, the development of polycystic ovary syndrome can also occur.
How to be diagnosed with polycystic ovary syndrome?
 In isolation, neither ultrasound (cystic-altered ovaries according to ultrasound), nor hormonal research, in which the indicators of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) are determined with the calculation of the ratio of LH / FSH, can be the only criteria for the diagnosis - "polycystic ovaries ". The situation is such that this diagnosis is made much more often than it actually occurs. Criteria for the diagnosis of polycystic ovary syndrome are divided into clinical, hormonal, ultrasound and histological.
In isolation, neither ultrasound (cystic-altered ovaries according to ultrasound), nor hormonal research, in which the indicators of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) are determined with the calculation of the ratio of LH / FSH, can be the only criteria for the diagnosis - "polycystic ovaries ". The situation is such that this diagnosis is made much more often than it actually occurs. Criteria for the diagnosis of polycystic ovary syndrome are divided into clinical, hormonal, ultrasound and histological. TO clinical symptoms polycystic ovary syndrome should include menstrual irregularities with no ovulation, the presence of hirsutism, an increase in body mass index of more than 25 points.
Ultrasound criteria (Ultrasound criteria) - a decrease in the size of the uterus in combination with an increase in the volume of the ovaries.
Hormonal criteria of this syndrome are as follows - hyperandrogenism (increased concentration of testosterone, dehydroepiandrosterone in the blood), an increase in the LH / FSH ratio of more than 2.5, a reduced content of progesterone in the luteal phase (second) of the menstrual cycle.
Histological criteria polycystic ovary syndrome - a study of the state of the mucous membrane of the uterine cavity after a separate diagnostic curettage of the uterine cavity and cervical canal reveals atrophic or dysplastic changes in the endometrium or, on the contrary, endometrial hyperplasia. Pathomorphological criteria - thickening of capillaries in ovarian tissue, thickening of the ovarian membrane, an abundance of maturing and atresing follicles (after surgical treatment).
Adrenal hyperandrogenism
 Forms of adrenal hyperandrogenism
Forms of adrenal hyperandrogenism
Consider now the increased production of androgens by the adrenal glands. As a rule, it occurs with congenital hyperplasia of the adrenal cortex. This pathology is a hereditary disease and is associated with a congenital defect in the enzyme systems necessary for the synthesis of sex steroid hormones. This defect can be complete or partial. With a complete defect, the body is not viable. With incomplete blockage as a result of interaction in the adrenal gland - hypothalamus - pituitary gland, excessive synthesis of androgens occurs with simultaneous hyperplasia (relatively speaking, an increase in volume) of the adrenal cortex. These disorders form the clinical picture of the specified syndrome.
Distinguish viril, salt-wasting and hypertensive forms hyperplasia of the adrenal cortex. We will dwell in more detail on the viril form of the syndrome of congenital adrenal hyperplasia.
Viril form of adrenal hyperandrogenism
This form is diagnosed in 90-95% of cases. The diagnosis can be made immediately after birth after examining the girl's genitals (enlarged clitoris, underdevelopment of the labia and others). However, in 43% of girls, the diagnosis is made with a significant delay. The reason for going to the doctor in these cases is the emerging signs of premature puberty, usually at the age of 4-5 years. The development of this syndrome at a later date indicates a latent or compensated impairment of androgen synthesis. As a rule, the impetus for the manifestation of the disease is stressful effects, neuroinfections, various intoxications, traumatic brain injuries, hormonal stresses (abortions, spontaneous abortions), and sometimes childbirth.There is a hereditary predisposition to congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Signs of burdened heredity are the presence in the family of stunted women with menstrual dysfunction, infertility, and impaired sexual development.
Treatment principles hyperandrogenism
 In the treatment of patients with polycystic ovary syndrome, great importance is attached to the correction of endocrine disorders - weight loss and the use of insulin-lowering drugs. In the presence of hyperprolactinemia (increased concentration of prolactin in the blood) - drugs of dopamine agonists, drugs of glucocorticoids and antiandrogens.
In the treatment of patients with polycystic ovary syndrome, great importance is attached to the correction of endocrine disorders - weight loss and the use of insulin-lowering drugs. In the presence of hyperprolactinemia (increased concentration of prolactin in the blood) - drugs of dopamine agonists, drugs of glucocorticoids and antiandrogens. First of all, to start treatment for polycystic ovary syndrome, it is necessary to normalize body weight. This is the first and key step in the treatment of this pathological condition, since the normalization of body weight will indirectly lead to the normalization of all types of metabolism. When drawing up a diet for weight correction, it is necessary to take into account the fact that the maximum calorie content of daily food should not exceed 2000 kcal. Moreover, the ratio of the main nutrients should be as follows: carbohydrates - 50%, proteins - 18%, fats - 32%. Moreover, 2/3 of the consumed fats should be represented by polyunsaturated fatty acids (omega-3, omega-6).
In the treatment of patients with congenital hyperplasia of the adrenal cortex, the main role is played by hormone replacement therapy. Treatment is most effective if started before age 7 years. For this purpose, glucocorticoid preparations are used.
It must be remembered that all issues related to the diagnosis and treatment of hyperandrogenism often lie within the competence of doctors of various specialties (gynecologists, endocrinologists, dermatologists, pediatricians), therefore, adequate therapy is the result of a comprehensive balanced approach to solving the diagnostic and therapeutic problem.
Lush, shiny and thick hair is not only the pride of every woman, but also one of the indicators of her health.
However, in this case we are talking about the scalp. But there are situations when hair begins to grow in other parts of the body, which is not normal for a woman's constitution. On the contrary, such a deviation may indicate very serious anomalies in the body, which the woman herself may not even know about.
In addition, excess vegetation on the body is a very unaesthetic phenomenon, which often leads to complexes and other psychological problems. But if a similar problem has already arisen, you do not need to despair and panic - you need to act immediately, because such a deviation may indicate the development of various diseases.
Let's try to find out what this anomaly is talking about, what caused it, and what methods can be used to defeat it.
The difference between hirsutism and hypertrichosis (excessive hair growth)
Hirsutism and hypertrichosis are concepts that are absolutely different from each other, so you need to learn to distinguish between them.
So, with hypertrichosis, the process of excessive growth of vellus hair occurs. However, it is not associated with an excessive amount of male sex hormones androgens in the blood of women, but may be due to:
- endocrine diseases (for example);
- taking some groups of medications (minoxidil, etc.);
- heredity;
- constitutional features of the female body.
In idiopathic hirsutism, there is no connection with hormonal balance in a woman's body. In addition, the presence of a small amount of hair above the upper lip, around the nipples, in the interval between the pubis and the navel is found even in girls who do not have problems with disorders in the endocrine system.
Note. Hirsutism is almost never a separate disease - in most cases it is a symptom of other pathologies. In particular, hyperandrogenism.
Hyperandrogenism - an increase in the concentration of androgens in the female body. It is with this phenomenon that the development of hirsutism is associated, which is its main difference from hypertrichosis. Hyperandrogenism is the result of disruption of the genital area in women, while the pathological process involves:
- hypothalamic-pituitary system;
- ovaries;
- adrenal glands.
Each of these pathologies has its own causes, understanding which, you can successfully get rid of an unpleasant problem. a
The main causes of facial hair growth in women
Even specialists cannot always answer the question of why facial hair grows in women. Of course, the first thing that comes to mind is a hormonal imbalance in the body. As you know, hormones affect the work of the whole organism, therefore, with their increased or, conversely, reduced concentration in the blood, not only internal organs, but also the epidermal integuments can react sharply.
Before determining the cause of increased facial hair, a woman should not independently diagnose herself, and even more so start treatment. First, you need to contact a gynecologist, endocrinologist, neuropathologist and go through all the necessary procedures aimed at identifying abnormalities in the work of internal organs, glands and systems. And only then the doctor will tell you what measures need to be taken to get rid of the unpleasant problem.
The appearance of facial hair in women is closely related to their health status. With an imbalance of internal organs, hair follicles react extremely sharply, which affects their functioning. The main causes of facial hair are:
- Increased concentration of the male sex hormone androgen... It is normally present in the female body, but in limited quantities, and affects fertility. In addition to the appearance of facial hair, a high level of testosterone in the blood in women can lead to the development of serious pathologies, therefore, it is necessary to consult an endocrinologist in a timely manner and start therapy.
- Genetic predisposition... If women in the family, be it a mother, grandmother or aunt, had problems with excess facial hair, then it is likely that other female generations will have a similar anomaly. In this case, no specific treatment is required - you can contact a beautician for help to perform hardware removal of facial hair.
- Impaired estrogen production... Estrogen is a female sex hormone that affects the menstrual cycle and the functioning of the entire reproductive system of a woman. After 35 years, the synthesis of this hormone slows down significantly, therefore, the body does not receive the required amount. As a result, hormonal changes occur. Also, with a decrease in the production of estrogen, the woman's body becomes more vulnerable to viral and bacterial infections. One of the most dangerous diseases is viral hepatitis. With its development, a woman develops black coarse hair on her chin. Such a deviation cannot be ignored, since viral hepatitis is a disease that can lead to death.
- may also be accompanied by the appearance of facial hair. This is due to the fact that the ovaries cease to function fully, and the level of sex hormones is significantly reduced. There is an increased production of male sex hormones androgens, which replace female ones - estrogens. This anomaly does not require specific treatment, and excess hairs can be easily removed using cosmetic or instrumental procedures.
- Hormonal imbalance during puberty in girls, as well as during pregnancy and lactation. As a rule, after the end of all the processes affecting the hormonal background of a woman, the level of hormones independently returns to normal.
- Taking hormonal drugs or long-term use of hormonal contraception. It's hard to imagine, but even hormonal creams can trigger unwanted facial hair in women. In this case, vellus hairs, or even white facial hair, may appear. After the termination of the use of the agent, which caused a sharp reaction of the body, the vegetation must pass by itself.

Symptoms
The main symptoms of hirsutism are:
- the appearance of hair on the face, inner thighs, buttocks, abdominal region, back, around the nipples, mammary glands;
- intense hair loss on the head, in particular in the frontal area;
- changing the type of skin and hair from normal, dry, or combination to oily;
- failure in the menstrual cycle;
- amenorrhea (prolonged absence of menstruation);
- the appearance of acne;
- inability to conceive a child.
Since the situation is caused by a hormonal imbalance, this deviation must be eliminated immediately. Otherwise, the so-called virilization may occur, which is characterized by:
- hair loss on the temples;
- a decrease in the tone of the voice when it becomes rough, masculine;
- reduction of mammary glands due to atrophy of glandular tissue;
- accumulation of fat cells in the tissues of the arms, legs, shoulders, chest;
- an increase in muscle tissue in the shoulder area (but can also be observed in other parts of the body);
- increased libido;
- reduction of the labia in size;
- enlargement of the clitoris;
- decreased production of vaginal lubrication.
How to stop facial hair growth
First of all, a woman needs to go to the hospital and undergo a comprehensive examination. Without knowing the reasons for the growth of facial hair, getting rid of them will be extremely problematic. The patient will first need to visit the gynecologist and endocrinologist's office.
Sometimes women have to undergo treatment for ovarian pathologies, including transferring the removal of neoplasms localized on them. Sometimes the increased facial hair indicates the formation of a tumor in the adrenal glands, which also requires surgical intervention.
With an overabundance of androgens, the doctor prescribes hormonal contraceptives or antiandrogenic agents. If facial hair in women appears during menopause, estrogen-based medications are prescribed.
If you do not normalize hormonal levels, the fight against facial hairs will become a grueling task. Moreover, you cannot pluck them out with tweezers or shave them off - they will be replaced by new, thicker and more bristly hair.

Treatment of excess facial hair growth
If hirsutism is mild and the woman has no changes in the menstrual cycle, treatment is not performed. However, this does not exclude the need for therapy for other diseases, since facial hair growth is only one of the symptoms of certain pathologies. In this case, the patient may undergo an operation to remove cysts or tumors in the pituitary gland, adrenal glands or ovaries.
It is also possible to cancel the medication that caused hirsutism, as well as to carry out treatment aimed at eliminating Itsenko-Cushing's syndrome or acromegaly. In simple terms, by eliminating the root cause, you can get rid of unwanted facial hair in women.
Medication can only be prescribed after a thorough examination. It is also extremely important to exclude the presence of androgen-secreting neoplasms. The use of hormonal drugs continues for 3 months to six months. In some cases, the course of treatment must be repeated.
When taking hormones, it must be borne in mind that they only prevent the growth of new hairs. Consequently, they have no effect on those that are already on the patient's face. Often, drugs are used to eliminate:
- Hyperandrogenism: Janine, Yarina,.
- Congenital adrenal hyperplasia:, Cortisone.
- : Yarina, Janine, Clomiphene.
- Tumors of various localization - ovarian, pituitary, adrenal. In this case, chemotherapy is used, as well as surgical removal of the neoplasm.
Contraindications to hormone therapy are:
- the presence of benign or malignant tumors of various localization;
- hypersensitivity to any components that make up the drug.
If hirsutism has caused weight gain, a low-carb diet should be followed. With manifestations of depression or neuroses, the patient may need the help of a psychologist or neuropathologist.
Cosmetological methods
With the help of modern cosmetics, you can, if not completely get rid of facial hair (although it is possible), then at least significantly reduce their visibility. However, they do not affect the further growth of hairs. Therefore, they can be used as adjunctive therapy.
Here are the main cosmetic methods of getting rid of facial hair in women:
- Lightening, which involves the use of products based on hydrogen peroxide and other substances, with the help of which there is a complete discoloration of facial hair, leading to the loss of their natural pigmentation.
- If the face is slightly damaged by hair, you can use the plucking method with tweezers. After the end of the painful procedure, the skin must be treated with an antiseptic. This will help avoid infection. However, this method cannot be abused - it can lead to problems with the epidermis.
- Shaving and waxing are also used to combat vegetation, but not on the face, but on the back, legs, armpits and groin. However, these methods cannot often be used, otherwise scars may form on the skin.
More expensive manipulations can also be performed:
- Photoepilation is a method based on the effect of high-pulse light rays on melanin, a pigment substance due to which the hair gets its natural color. The heat effect destroys the hair follicle, which leads to the removal of hairs. The method is used for dark hair, and the effect of its use lasts about 5 months.
- Laser hair removalbased on the use of a laser beam. Removes only growing hairs without affecting dormant bulbs. For this reason, it is necessary to carry out several manipulations within 1-6 months. Laser hair removal is less effective than photo hair removal.
Laser and photoepilation cannot be performed if there are the following contraindications:
- the presence of inflammatory processes in the problem area;
- pregnancy;
- prolonged exposure to ultraviolet rays before the procedure;
- the presence of a tattoo in the area of \u200b\u200bhair growth;
- undergoing a course of therapy using steroids or isotretinoin;
- have a pacemaker or insulin pump;
- porphyria.
Since laser and photoepilation are expensive procedures, it is advisable to carry them out only to remove hair in open areas of the body. However, be prepared for the fact that the manipulations will need to be repeated from time to time, since they do not affect further hair growth.

Folk ways to get rid of hair
Alternative methods can be used as auxiliary therapeutic procedures:
- Datura decoction - a medicinal plant containing a poison that negatively affects the structure of the hair follicle. Rinse 3-4 plants with roots and cover with a liter of water. Bring to a boil, then simmer over low heat for an hour. Strain the finished broth and use it as a tonic for rubbing into the skin after depilation.
- Squeeze half a lemon into a glass, add 1 spoonful of sugar and put on low heat. Wait until half of the liquid has evaporated, then cool - and problem areas can be treated. After 2 minutes after treatment, rinse off the remnants of the product with warm water.
- Squeeze out as much juice as possible from the peel of a green walnut and apply it through cheesecloth to problem areas of the skin and keep for 5 minutes. With intensive hair growth, the product should be used twice a day. It is allowed to be applied to any part of the body.
Treatment for hirsutism is not limited to the symptomatic approach. In this case, it is necessary to understand the cause of the deviation and eliminate it, and this can only be done by a doctor.
Disease prognosis
The life cycle of a hair lasts six months, and it is during the same period of time that hirsutism therapy lasts. Even if it is not possible to completely get rid of the growth of unwanted hair in women, then it is quite possible to significantly slow down this process and make the hairs lighter.
The growth of body hair is normal, and moderate vegetation in certain areas of the body indicates the health of the body. However, too much body hair growth or sudden hair loss can be caused by a number of factors indicating some health problems that need to be urgently addressed with the help of a doctor. So, what can cause increased body hairiness or sudden loss of body hair? Let's take a look at several reasons.
1. Genetic predisposition
How much body hair grows can depend on your genetic makeup and nationality. Too dense vegetation on the body is usually characteristic of people of southern and eastern blood. The hairs of representatives of "hot" nationalities are usually dark, thick and coarse, so in their case there is no need to worry about their presence. If you do not ethnically belong to the eastern and southern peoples, and your parents do not have dense tough vegetation, then the sudden appearance of thick dark hairs on your body may indicate hormonal disorders, especially if you were not previously prone to increased hairiness.
2. Autoimmune disorders
Sometimes, malfunctioning of the immune system can affect the functioning of hair follicles. In this case, there may be a sharp loss of hair on the head and body in whole handfuls, "bald spots" are formed in certain areas or throughout the head and body. Such disorders are treated with systemic steroids, but it is not always possible to restore the vegetation completely.
3. Hormonal disorders
A sudden increase in body hairiness or sudden loss of body hair can be the result of a disruption in the production of male hormones in the body in both men and women. If testosterone levels are above normal, then body hairiness increases dramatically, and hair begins to become darker, coarser and thicker, and can also begin to grow even in areas where they were not previously. A sudden loss of body hair may indicate a sharp change in the production of female hormones, which is also not favorable for your body. In both cases, it is necessary to contact an endocrinologist to prescribe the appropriate treatment with hormonal drugs.
4. Problems with the ovaries in women
If women experience irregular critical days in addition to increased body hair, this is most likely indicative of ovarian problems. Most often, increased hairiness in combination with irregular periods indicates the presence of a disease such as polycystic ovary syndrome. In this case, in addition to the above symptoms, there is also a sharp increase in weight. Contact your doctor immediately for timely treatment.
5. Tumor
A sharp and sudden increase in body vegetation may be a sign of a tumor in your body. As a rule, in this case, the tumor most often affects the adrenal glands or ovaries, so it is necessary to examine these glands with particular care.
6. Iron deficiency or thyroid disorder
A sudden loss of hair on the head and body can indicate a lack of iron in the body or thyroid disorders. Most often, iron deficiency affects people who abruptly switch to vegetarianism. Thyroid disorders are often accompanied by shedding of the eyebrows, grooving on the nails, and severe baldness of the head and body. In this case, it is necessary to urgently donate blood for analysis and begin treatment of the thyroid gland. Also, sudden hair loss can be observed in women due to pregnancy or abrupt cessation of contraception. In this case, hair loss is short-term, and does not require enhanced medication treatment.
7. Bad habits
Smoking and the use of drugs lead to the death of hair follicles, since the nutrients necessary for the nutrition and growth of hair are not supplied to the hair follicles and hair roots. The obvious solution to the problem of baldness in this case is to stop smoking or taking drugs.








What to give a vegetarian for his birthday
Face cream at home - preparation rules
An ancient recipe for youth from Tibetan monks
How to drink clay to cleanse the body
Download maps slavic oracle